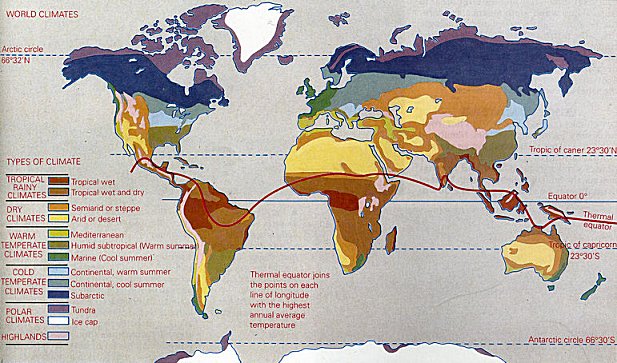
World Climate
The Hot, Wet Equatorial Climate
Distribution:- It is found between 5° and 10° north and south of the equator.
- It is dominantly found in the lowlands of the Amazon, the Cango, Malaysia and the East Indies.
- There is great uniformity of temperature through out the year.
- The mean monthly temperatures are always around 24 to 27°C, with very little variation.
- There is no winter.
- Precipitation is heavy between 60 inches and 10 inches, and well distributed throughout the year.
- It support a luxuriant type of vegetation - the tropical rain forest.
- Amazon tropical rain forest is known as Selvas.
- It comprises a multitude of evergreen trees that yield tropical hardwood, e.g. mahogany, ebony, greenheart, cabinetwood, and dyewoods.
- In the forests, most primitive people live as hunters and collectors and the more advanced ones practice shifting cultivation.
- Some plantation crops are also practiced like natural rubber, cocoa, etc.
The Tropical Monsoon and Tropical Marine Climates
Distribution:- It is found in the zones between 5° and 30° latitudes on either side of the equator.
- It is best developed in the Indian subcontinent, Burma, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, parts of Vietnam and South China and northern Australia.
- Tropical Marine climate is found in Central America, West Indies, the Philippines, parts of East Africa, West Indies, the Philippines, parts of East Africa, Madagascar, the Guyana coast and eastern Brazil.
- Though mean annual temperature is fairly high but summer and winter seasons are sharply differentiated due to northward and southward movement of the sun.
- The average annual rainfall is around 150 cm but there are much variations in the temporal and spatial distribution.
- Most of the forests yield valuable timber like teak. Other kinds of timber are sal, acacia and eucalyptus.
- People are mainly engaged in agriculture.
The Hot Disert and Mid-Latitude Desert Climates
Distribution- The major hot deserts of the world are located on the western coasts of continents between latitudes 15° and 30°N and S.
- The relative humidity is extremely low, decreasing from 60 per cent in coastal districts to less than 30 per cent in coastal districts to less than 30 per cent in the desert interiors.
- Rain normally occurs as violent thunderstorms of the convectional type.
- The highest shade temperature recorded is 136°F on the 13 September 1922 at Al Azizia, 25 miles south of Tripoli, Libya, in the Sahara.
- All deserts have some form of vegetation such as grass, crub, herbs, weeds, roots or bulbs.
- The Bushmen of the Kalahari and the Bindibu of Australiar remain so primitive in their mode of living that they barely survive.
- Both the tribes are nomadic hunters and food gatherers, growing no crops and domesticating no animals.
Mediterranean Climate
Distribution- This climate type prevails in much of California, in parts of Western and South Australia, in southwestern South Africa and in parts of central Chile.
- The climate is characterized by hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters.
- Since all regions with a Mediternean climate are near large bodies of water, temperatures are generally moderate with a comparatively small range of temperatures between the winter low and summer high.
- During summer, regions of Mediterranean climate are dominated by subtropical high pressure cells causing no or little rainfall.
- During winter the polar jet stream and associated periodic storms reach into the lower latitudes of the Mediterranean zones, bringing rain, with snow at higher elevations.
- Evergreen coniferous trees are pines, firs, cedars and cypresses.
- Nowadays, the area is important for fruit cultivation, cereal growign, wine-making and agricultural industries as well as engineering and mining.
- The Mediterranean lands are also known as the worl's orchard lands.
- Cereals are also grown in the Mediterranean lands. Wheat is the leading food crop. The wheat grown is mainly hard, winter wheat.
The Savanna or Sudan Climate
Distribution- It is located between 5°-20° latitudes on either side of the equator.
- The most characteristic areas of savanna climate include the Llanos of Orinico valley, the Campos of Brazil, hillyareas of central America, southern Zaire, etc.
- The Savanna climate is characterized by distinct wet and dry seasons.
- Mean high temperature throughout the year is between 24°C and 27°C.
- The average annual rainfall ranges between 100 cm and 150 cm.
- It is characterized by tall grass and short trees.
- Some tribes live as pastoralists like the Masai and other as settled cultivators like the Hausa of northern Nigeria.
- However, agriculture is not much developed.
The Temperate Continental (Steppe) Climate
Distribution- Bordering the deserts, away from the Mediterranean regions and in the interiors of continents are the temperate grasslands.
- In Eurasia, they are called the Steppes.
- Their climate is continental with extremes of temperature.
- Summers are very warm.
- Winters are very cold in the continental steppes of Eurasia.
- The average rainfall may be taken as about 20 inches.
- The term 'steppe vegetation' geographically refers to the scanty vegetation of the subarid lands of continental Eurasia.
- Their greatest difference from the tropical savanna is that they are practically treeless and the grasses are much shorter.
- The grasslands have been ploughed up for extensive, mechanized wheat cultivation and are now the 'granaries of the world'. Besides wheat, maize is increasingly cultivated in the warmer and wetter area.
Warm Temperate Eastern Margin (China Type) Climate
Distribution- This type of climate is found on the eastern margins of continents in warm temperate latitudes, just outside the tropics.
- It is, in fact, the climate of most part of China-a modified form of monsoonal climate. It is thus also called the (Temperate Monsoon) or China Type of climate.
- The Warm Temperate Eastern Margin Climate is typified by a warm moist summer and a cool, dry winter.
- The mean monthly temperature varies between 40°F and 78°F and is strongly modified by maritime influence.
- Rainfall is more than moderate, anything from 25 inches to 60 inches.
- The eastern margins of warm temperate latitudes have a much heavier rainfall than either the western margins or the continental interiors and thus have a luxuriant vegetation.
- Conditions are well suited to a rich variety of plant life including grass, ferns, lianas, bamboos, palms and forests.
- Rice, tea and mulberries are extensively grown in monsoon China.
- Elsewhere are found other products of economic importance, e.g. can sugar in Natal, coffee and maize in South America and dairying in New South Wales and Victoria.
The Cool Temperate Western Marigin Climate
Distribution- The cool temperate western margins are under the permanent influence of the Westerlies all round the year.
- From Britain, the climatic belt stretches far inland into the lowlands of North-West Europe, including such regions as northern and western France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Denmark, western Norway and also northwestern Iberia.
- There is so much oceanic influence on both the temperature and the precipitation that the climate is also referred to as the North-West European Maritime Climate.
- In the southern hemisphere, the climate is experienced in southern Chile, Tasmania and most parts of New Zealand, particularly in South Island.
- The mean annual temperatures are usually between 45°F and 60°F.
- The British type of climate has adequate rainfall throughout the year with a tendency towards a slight winter or autumn maximum from cyclonic sources.
- The deciduous hardwoods are excellent for both fuel and industrial purposes.
- A very large part of the deciduous woodlands have been cleared for fuel, timber of agriculture.
- Fishing is particularly important in Britain, Norway and British Columbia.
- Throughout Britain and northwestern Europe, farmers practice both arable farming and pastoral farming.
The Cool Temperate Continental Climate
Distribution- The Cool Temperate Continental (Siberian) Climate is experienced only in the northern hemisphere where the continents within the high latitudes have a board east-west spread.
- The climate of the Siberian type is characterized by a bitterly cold winter of long duration, and a cool brief summer.
- An annual range of 54°F is common in the Siberian type of climate.
- The extremes of temperature are so great in Siberia that it is often referred to as the cold 'pole of the earth'.
- Some of the lowest temperatures in the world are recorded in Verkhoyansk.
- In winter the precipitation is in the form of snow.
- The coniferous forest belts of Eurasia and North America are the richest sources of softwood.
- There are four major species in the coniferous forests.
- Pine e.g. white pine, red pine, Scots pine, Jack pine, lodgepole pine.
- Fir e.g. Doublas fir and balsam fir, Spruce
- Larch
- The various species of pine, fir, larch and spruce are felled and transported to the saw-mills for the extraction of temperate solft-woods.
The Cool Temperate Eastern Margin
Distribution- The Cool Temperate Eastern Margin (Laurentian) Climate is an intermediate type of chmate between the British and the Siberian type of climate.
- It has features of both the maritime and the continental climates.
- Laurentian type of chmate is found only two regions. One is north-eastern North America, including eastern Canada, north-east USA. This may be referred to as the North American region. The other region is the eastern coastlands of Asia, including eastern Siberia, North China, Manchuria, Korea and northern Japan. It may be referred to as the Asiatic region.
- The Laurentian type of climate has cold, dry winters and warm, wet summers.
- Summers are as warm as the tropics (70°-80F).
- Of the annual precipitation of 30 to 60 inches, two-thirds come in the summer.
- Generally the forest tend to be coniferous north of the 50°N parallel of latitude.
- Lumbering and its associated timber, paper and pulp industries are the most important economic undertaking.
The Arctic or Polar Climate
Distribution- The polar type of climate and vegetation is found mainly north of the Arctic Circle in the northern hemisphere.
- The ice-caps are confined to Greenland and to the highlands of these high-latitude regions where the ground is permanently snow-covered.
- Winters are long and very severe, summers are cool and brief.
- At the North Pole, there are six months without light in winter.
- There are no trees in the tundra.
- Human activities of the undra are largely confined to the coast.
- The few people who live in the tundra five a semi-nomadic life.
- In Greenland, northern Canada and Alaska five the Eskimos.
- They used to live as hunters, fishers and food-gatherers.
Author


Comments
Post a Comment